Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Market Categories and Deployment Types
- Decision Criteria Comparison
- GigaOm Radar
- Solution Insights
- Analyst’s Outlook
- Methodology
- About Ivan McPhee
- About GigaOm
- Copyright
1. Executive Summary
The network operating system (NOS) landscape is evolving rapidly to address new demands reflected by new acquisitions, new capabilities, new investors, new partnerships, and new customer engagements. Legacy vendors have adopted disaggregation to protect their installed base and mitigate supply chain issues; open source initiatives promise flexible, low-cost deployments with rapid community innovation; and new players have emerged with disruptive, cloud-native approaches, significant financial backing, and high-profile early adopters.
The result? A market defined by limited choice and “few sizes fit all” solutions has been replaced by disaggregated, cost-efficient, open-standards-based, interoperable tech stacks. Instead of purchasing and deploying a “best-fit” solution, customers can independently choose—and swap out—hardware and software based on what makes the most sense for each use case. In addition, disaggregation enables users to tailor their networks to the exact needs of their operations by adding or removing specific features, eliminating expensive forklift upgrades, and limiting vulnerabilities and risk exposure.
Moreover, telecommunications service providers—including mobile network operators (MNOs) who provide wireless voice and data communication for their subscribed mobile users and network service providers (NSPs) that own, operate, and sell access to internet backbone infrastructure and services—have experienced a paradigm shift from traditional, monolithic network models to a more modular and flexible framework.
Disaggregation allows MNOs and NSPs to choose from a broader range of vendors and tailor their network architecture to their specific needs. In addition, disaggregation breaks vendor lock-in, allowing service providers to select hardware and software components from different vendors and reduce the total cost of ownership (TCO) with pay-as-you-grow models involving lower upfront costs (CapEx) and recurring costs (OpEx). Furthermore, disaggregated networks offer scalability to almost any size and adaptability to changing business needs, enhancing management processes by enabling individual network components to be updated and upgraded.
As a result of these myriad benefits, disaggregated NOSs have become critical for managing complex networking infrastructures supporting extensive communication, data sharing, and application services. They deliver enterprise-level management to ensure high availability, resilience, and security, which are essential for the smooth operation of service provider networks. Furthermore, NOSs enable providers to offer improved performance, reliability, and cost-effective scalability, which are critical for industries with fluctuating demands or rapid growth.
As networking demands evolve, NOS vendors innovate rapidly to deliver the tools needed for efficient network management. When selecting a NOS, service providers should look for a solution that facilitates efficient network management, enhances security, promotes collaboration, and supports business growth and evolution. In addition, they should consider the size of their enterprise, existing infrastructure, compatibility, technical expertise, budget, and networking requirements.
This is our fourth year evaluating the NOS space in the context of our Key Criteria and Radar reports. This report builds on our previous analysis and considers how the market has evolved over the last year.
GigaOm Radars for Network Operating Systems
Due to the large number of suppliers and solutions available, we have divided the NOS landscape into three reports based on the target market.
- Mobile network operators (MNOs) and network service providers (NSPs), often referred to as “telco service providers”
- Cloud and managed service providers (CSPs and MSPs)
- Large enterprises and small-to-medium businesses (SMBs)
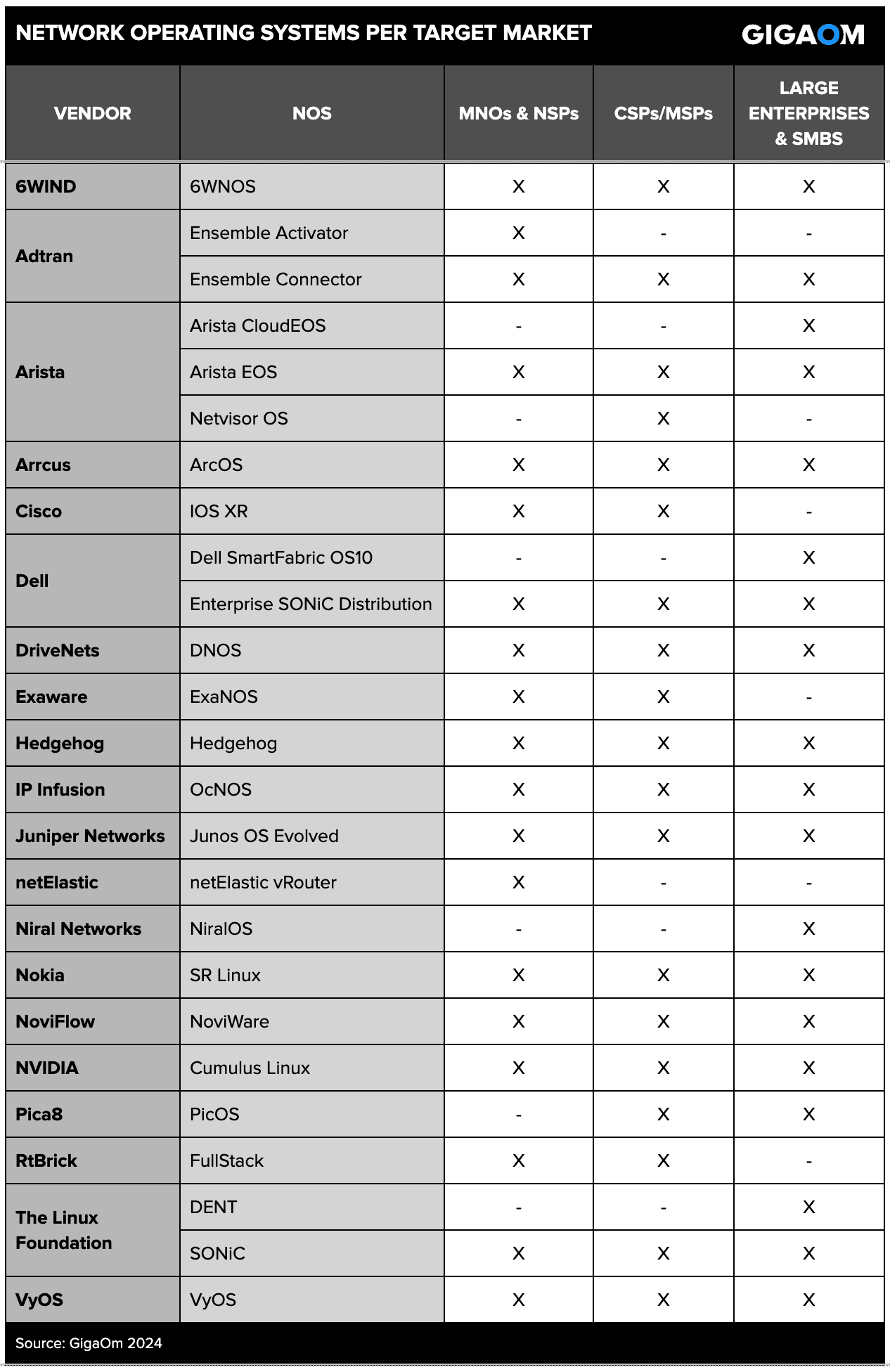
Figure 1 indicates which vendors and NOSs are covered in each report. YoY changes relating to the vendors and solutions we evaluated are covered in section 4. “GigaOm Radar.”
Figure 1. Suppliers and NOSs included in each GigaOm Radar
This GigaOm Radar report evaluates 19 of the top NOSs and compares offerings against the capabilities (table stakes, key features, and emerging features) and nonfunctional requirements (business criteria) outlined in the companion Key Criteria report. Together, these reports provide an overview of the market, identify leading NOSs, and help decision-makers evaluate these solutions to make a more informed investment decision.
GIGAOM KEY CRITERIA AND RADAR REPORTS
The GigaOm Key Criteria report provides a detailed decision framework for IT and executive leadership assessing enterprise technologies. Each report defines relevant functional and nonfunctional aspects of solutions in a sector. The Key Criteria report informs the GigaOm Radar report, which provides a forward-looking assessment of vendor solutions in the sector.