Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- SMP Sector Brief
- Decision Criteria Analysis
- Analyst’s Outlook
- Methodology
- About Matt Jallo
- About GigaOm
- Copyright
1. Executive Summary
Software as a service (SaaS) applications represent 50% or more of most companies’ application portfolios. These applications require new operating procedures for managing spending, contract renewals, user lifecycles, and security controls.
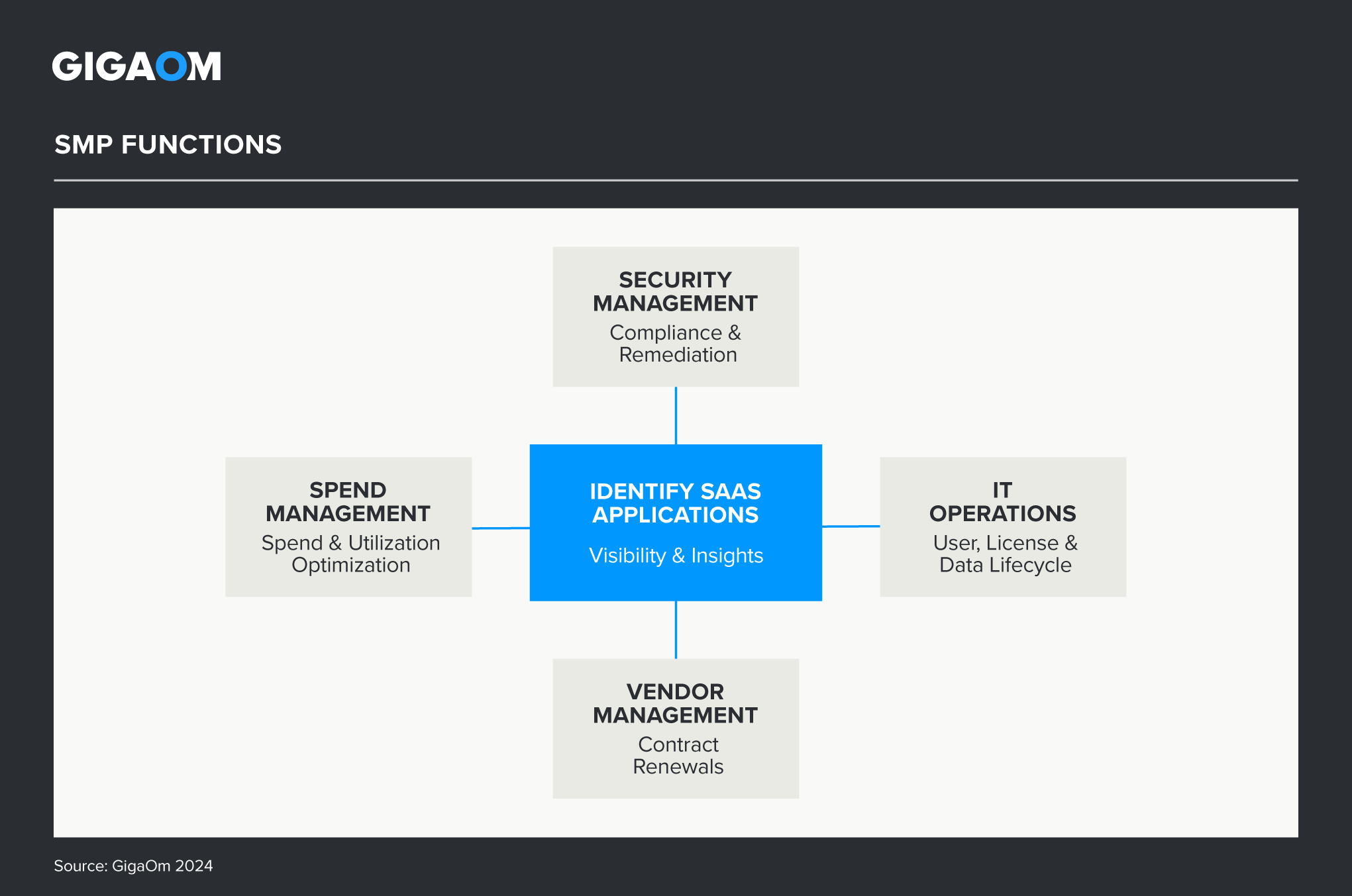
As Figure 1 shows, SaaS application management platforms (SMPs) enable more efficient operations by consolidating cost and application usage data through integration, creating an application inventory, identifying contract entitlements and cost savings, automating operational lifecycles, and enforcing security controls.
Figure 1. SMP Functions
SaaS applications require standard processes to address spending, operational, and security challenges. Unnecessary costs may be incurred by over-committing to contract entitlements or maintaining redundant or underused applications. Operational overhead can snowball when access, licensing, and user requests are managed manually with no time for proactive trimming the inventory of existing applications. Security risks escalate without proactive monitoring and remediation to protect sensitive data being stored in the applications.
Small-to-medium businesses (SMBs) and large enterprises alike benefit from investing in an SMP:
- SMPs use discovery to create an application catalog with visibility into all applications in use. The catalog enables collaboration and shared accountability across finance, IT, security, and sourcing departments for cost savings and operational efficiency. It is enriched with application spend, licensing, and usage data obtained directly from the managed applications.
- Spend management enables cost savings by identifying opportunities to reduce application usage. Contract management enables cost savings by determining where and when to cut or cross-level an entitlement.
- Operational efficiencies are achieved by using workflow automation to offload operations from people performing repetitive tasks. Security risks are reduced by leveraging application integration to identify locations where sensitive data is stored and using workflow automation to remediate access to exposed sensitive data.
Business Imperative
SaaS applications are easy to start using; in many cases all that is needed is a credit card and an internet connection. While this is a great model in terms of deployment and accounting, it makes it more difficult for IT to manage the application portfolio. The effects of this can be severe; at times, organizations may be paying too much due to a lack of volume licensing or lax management of unused licenses, or an inability to anticipate usage may lead to hardware and networking shortfalls. Even worse, sensitive company data may make its way into the wrong hands or properly secured identity providers go unused and no record is kept of access to important systems.
An inability to manage an organization’s SaaS applications makes it even more difficult for IT to partner with business units. Beyond saving money and mitigating risk, SaaS management platforms make it easy for employees to access the software that they need when they need it, alleviating a common frustration that organizations have experienced in the age of digital work.
Sector Adoption Score
To help executives and decision-makers assess the potential impact and value of an SMP deployment to the business, this GigaOm Key Criteria report provides a structured assessment of the sector across five factors: benefit, maturity, urgency, impact, and effort. By scoring each factor based on how strongly it compels or deters adoption of a SMP, we provide an overall Sector Adoption Score (Figure 2) of 4.6 out of 5, with 5 indicating the strongest possible recommendation to adopt. This suggests that an SMP is a very credible candidate for deployment and worthy of thoughtful consideration.
The factors contributing to the Sector Adoption Score for SMPs are explained in more detail in the Sector Brief section that follows.
Key Criteria for Evaluating SMPs
Sector Adoption Score
Figure 2. Sector Adoption Score for SMPs
This is the third year that GigaOm has reported on the SMP space in the context of our Key Criteria and Radar reports. This report builds on our previous analysis and considers how the market has evolved over the last year.
This GigaOm Key Criteria report highlights the capabilities (table stakes, key features, and emerging features) and nonfunctional requirements (business criteria) for selecting an effective SMP. The companion GigaOm Radar report identifies vendors and products that excel in those decision criteria. Together, these reports provide an overview of the market, identify leading SMPs, and help decision-makers evaluate these solutions so they can make a more informed investment decision.
GIGAOM KEY CRITERIA AND RADAR REPORTS
The GigaOm Key Criteria report provides a detailed decision framework for IT and executive leadership assessing enterprise technologies. Each report defines relevant functional and nonfunctional aspects of solutions in a sector. The Key Criteria report informs the GigaOm Radar report, which provides a forward-looking assessment of vendor solutions in the sector.