Table of Contents
1. Executive Summary
Data is core to all organizations and should be treated as an essential asset. As the data landscape continues to evolve, data is increasingly dispersed across many locations. No longer limited to on-premises shares and databases, it is stored across many cloud repositories and data platforms.
This changing landscape and business demands for how data is used have increased both its value and the impact of its loss. This has not gone unnoticed by cybercriminals, with data being the ultimate goal for most cyberattacks. Whether it is the theft of this data, denying access to it, or a mix of both, data is a valuable asset for owners and criminals alike. The diligent business must take the security of its data seriously for technical, commercial, and regulatory reasons. Data security cannot go unchecked, as the impact of a data loss incident can be severe.
Addressing this threat is not a technology challenge alone. Businesses must ensure that data management processes are comprehensive and understood. People must be educated about the impact of data security breaches and the part they play in protecting data assets. However, this cannot be achieved without the use of technology. Improving a business’s data security posture has led to the development of data security posture management (DSPM) solutions. DSPM solutions are designed to provide full visibility into data across an entire organization. They provide insight into data use and risks associated with how it is stored, used, and accessed. They provide guidance on how an organization’s handling of data aligns with regulatory demands. They can also provide detailed guidance on how to address these risks and threats and apply controls to mitigate and reduce them.
Business Imperative
Data is too key an asset for any organization to fail to take data security seriously. Data security is not an IT-only issue—it is a broad business issue—and should never be an IT-only project or responsibility. However, those in charge of organizational IT are central to protecting data and ensuring it is well-secured.
DSPM solutions can be a powerful component of addressing the risks to an organization’s data assets. They can provide proactive, detailed insight into all data locations, including shadow, dormant, and redundant data that otherwise goes unnoticed and unsecured. DSPM provides a business with a measurable baseline to understand the current posture, steps to improve it, and ongoing monitoring of data usage, access, and risk. In a world where organizations are compelled to comply with increasingly stringent regulations, these types of tools are critical.
However, those charged with data security must also appreciate that the adoption of DSPM solutions is not trivial. DSPM solutions are likely to show risks in the way data is created, stored, and used, and these identified risks are likely to require changes in process—impacting current workflows—and culture. This is why DSPM adoption must be a business initiative and not just a technical one.
Sector Adoption Score
To help executives and decision-makers assess the potential impact and value of a DSPM solution deployment to the business, this GigaOm Key Criteria report provides a structured assessment of the sector across five factors: benefit, maturity, urgency, impact, and effort. By scoring each factor based on how strongly it compels or deters adoption of a DSPM solution, we provide an overall Sector Adoption Score (Figure 1) of 3.2 out of 5, with 5 indicating the strongest possible recommendation to adopt. This indicates that a DSPM solution is a credible candidate for deployment and worthy of thoughtful consideration.
The factors contributing to the Sector Adoption Score for DSPM are explained in more detail in the Sector Brief section that follows.
Key Criteria for Evaluating DSPM Solutions
Sector Adoption Score
Figure 1. Sector Adoption Score for DSPM
This is the first year that GigaOm has reported on the DSPM space in the context of our Key Criteria and Radar reports. This GigaOm Key Criteria report highlights the capabilities (table stakes, key features, and emerging features) and nonfunctional requirements (business criteria) for selecting an effective DSPM solution. The companion GigaOm Radar report identifies vendors and products that excel in those decision criteria. Together, these reports provide an overview of the market, identify leading DSPM offerings, and help decision-makers evaluate these solutions so they can make a more informed investment decision.
GIGAOM KEY CRITERIA AND RADAR REPORTS
The GigaOm Key Criteria report provides a detailed decision framework for IT and executive leadership assessing enterprise technologies. Each report defines relevant functional and nonfunctional aspects of solutions in a sector. The Key Criteria report informs the GigaOm Radar report, which provides a forward-looking assessment of vendor solutions in the sector.
2. DSPM Sector Brief
Data security risks cannot go unchecked within an organization. The loss of data—whether this is data taken from an organization or data that is made no longer accessible to an organization—has a significant impact on a business technically, commercially, and for those who find themselves in breach of regulation, legally.
Organizations must tackle data security, and they can only do so if they understand the overall posture of their data security at a given time. To do this, the organization must understand what data it has and the sensitivity of the data—containing personal, financial, or health information, for example. It must also know where the data is held, who has access to it, and why and when they are accessing it.
Without this information, organizations are blind to any risk and are prone to potential data security breaches. With this information, the organization can begin to understand whether there is risk associated with its current data handling infrastructure, processes, and policies. Organizations should understand that today, the risk of a data breach is high. However, since there are tools and steps that can be taken to reduce risk, organizations that are seen as failing to do so will not be looked at sympathetically.
Scenarios for Adoption
DSPM solutions have value across many scenarios, but there are use cases where they are particularly relevant.
The primary customer is organizations that operate in highly regulated industries like financial, healthcare, government, pharmaceuticals, or any that are holding data that falls under privacy regulations around the world. For these organizations, DSPM should be a priority.
Additionally, larger organizations with more complex data infrastructure should also have tools that help them to understand what data and datasets they control and how that data is used. These organizations have data that’s spread across many locations, and DSPM tools can prove highly valuable by simply providing visibility into data holdings.
Lastly, a rapidly growing use case is in the increasing use of AI tools. Businesses pointing learning models at their datasets must take appropriate actions to cover several potential risks. This includes ensuring that the data fed to these learning models is clean and relevant. They must ensure that data is only accessed by those who have the right to do so. They must also understand when AI training models are accessing data and what data they are accessing. This should be a primary concern for any business adopting AI models at scale.
Adoption Approach
The approach to adopting DSPM cannot be an IT-led initiative alone. Data security is a business issue and one that impacts an organization’s business governance and compliance. It must be a task that is shared from the board level and C-suite to individual contributors. Therefore, the first step of any DSPM adoption must be business-wide education and commitment. The adoption of DSPM can have broad consequences in the way a business interacts with its data and must be supported across the organization for successful adoption.
With business commitment, initial adoption can be straightforward. Many solutions are cloud-based and are enabled without the use of agents or any other tools that sit in the line of data access. The initial evaluation will create visibility into data across the organization, providing insight into data types and usage and highlighting risks. Organizations should be aware that some of the identified risks may be sensitive, showing poor data usage by senior leaders.
Once risks are identified, organizations can begin addressing them. Many leading solutions will provide detailed guidance on how to achieve this, but businesses should be prepared for the impact on day-to-day operations of changes to the way data is stored, used, and shared.
Adopting DSPM is as much about culture as technology and the diligent leader will prioritize preparation and education ahead of any technical deployment.
Technical Primer
DSPM solutions are often cloud-based and designed to integrate with a wide range of data repositories. Typically, they will be able to discover data repositories automatically, including unused, dormant, and shadow repositories. They will build a data map, and they will analyze data movement and lineage to understand how the data flows through an organization and where it may introduce risk. The solution will use this information to help provide an organization with a clear visualization of its data estate, its compliance position, and its security posture.
Crucially, once deployed, DSPM solutions should continuously monitor security posture, provide guidance on access controls, understand user behavior to quickly identify threats, and allow an organization to mitigate them rapidly.
Most solutions in this space require little in the way of infrastructure, as they are mainly provided as SaaS and don’t require agents or proxies to integrate with data repositories. Cloud-based data integration is usually via API. On-premises environments are more likely to require some kind of scanning agent and to need configuration rather than auto-discovering data.
Solutions should be capable of integrating with the wider enterprise technology ecosystems including security information and event management (SIEM), security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR), and IT service management (ITSM) platforms to ensure they are part of the general IT operations workflow. Some solutions are also capable of automating the response to risk and threat. However, as with all automation tools, organizations should be clear about the impact that automated mitigation may have on existing processes and workflows.
Technical adoption of DSPM solutions for posture reporting will be straightforward in most cases. However, consideration should be given to any mitigation steps they can take, along with the impact of data classifications and more stringent control that will be applied to data and its usage. Automated threat detection and response capabilities offered by a solution may have impacts that require consideration.
Sector Scorecard
In the Executive Summary, we introduced a Sector Adoption Score that provides a high-level grade indicating how compelling and appropriate an enterprise technology may be for adoption. The score is based on five factors and how strongly each compels or deters adoption of the technology.
The Sector Scorecard (Figure 2) provides an at-a-glance assessment of the adoption ratings for these factors as they relate to DSPM:
- Benefit to the organization
- Urgency as defined by competitive, market, regulatory, and other pressures
- Impact on IT staff, users, and budgets
- Effort required to address the complexity and challenges of deployment
- Maturity and relative stability of the technology sector
Key Criteria for Evaluating DSPM Solutions
Adoption
Rating
Compels
Adoption
Encourages
Adoption
Merits
Consideration
Discourages
Adoption
Deters
Adoption
Sector Scorecard Sector Scorecard Considerations
Benefit
- Compelling ROI
- Reduced costs
- Heightened productivity and efficiency
- Enhanced resilience
Urgency
- Competitive pressure
- Security vulnerabilities
- Regulatory compliance
- Aging infrastructure
- Staffing/skills challenges
Impact
- Staff and end-user training
- Hiring and workforce alignment
- Licensing and operating costs
Effort
- Business-critical systems and processes
- Custom development
- Required integration
Maturity
- Established vendors
- Volatility of technology
- Access to skilled workers
- Presence of industry standards
Considerations
Figure 2. Sector Scorecard for DSPM
Benefit: Encourages Adoption
Data needs to be secured, as the risks of failing to do so are too high. DSPM solutions provide insights into risk and vulnerability and can provide alerts about active risks. Adopting a DSPM solution carries great benefits and will help reduce the risk, as well as the impact, of any potential data incident.
Urgency: Encourages Adoption
Leaving data at risk—whether it is security or compliance-related risk—is not acceptable. The impact of a data breach is wide-ranging and will have technical, commercial, and legal ramifications that cannot be ignored by any diligent business.
Impact: Merits Consideration
A full DSPM adoption is no small task. Organizations will likely need to adopt new processes, including data classification, data loss controls, and adherence to data security and privacy regulations. It will require training of users, culture change, and new working practices. Adoption is not trivial and organizations must be prepared for the work required to successfully apply DSPM-based data controls.
Effort: Discourages Adoption
There is no doubt that adopting a DSPM platform is likely to highlight issues in the way an organization manages its data. It will show potential risks and will likely demand changes—both technical and organizational. There will be work to do in training users, but also integrating the platform across data sets and taking the time to understand the outputs. DSPM adoption is not a trivial task, and a business must understand the effort required and be both prepared and willing to meet the demands of DSPM adoption.
Maturity: Merits Consideration
DSPM is still an evolving discipline. While some of the component parts are established, some approaches are not yet consistently defined. While areas such as classification are not new and are well-defined, features like threat scoring are not. The maturity question is not one just for the vendor. DSPM is a business-wide discipline; therefore, organizations must understand their maturity and ability to adopt such technology.
Sector Scorecard Summary
The need for improved data security should be paramount in all organizations. However, data security can be complex. While the use of DSPM to provide a view of data security posture does not need to be complex, the steps needed to adopt the outcome of initial DSPM discovery will challenge organizations. Organizations will need a mature understanding of data risk and what addressing it means. They will need to have a culture of data security and understand why it is important. Adoption processes that will improve data posture will require support across an organization including broad education of users, changes to work processes, and time to develop, understand, and deploy both technical and policy solutions.
Those who adopt DSPM will have strong external drivers that demand it. Those in heavily regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, or local government have the most obvious demand for a strong data security posture. Equally, those handling large amounts of personal data or businesses with intellectual property that differentiates it from its competitors will benefit from a DSPM solution. There is also a rapidly developing use case for businesses looking to adopt AI. The need to properly govern what data learning models can access is likely to drive an uptick in DSPM adoption.
To facilitate the DSPM solution selection process, this Key Criteria report acts as a buyer’s guide for IT decision-makers, exploring the table stakes, key features, emerging features, and business criteria that are relevant to a purchase decision.
3. Decision Criteria Analysis
In this section, we describe the solution capabilities—table stakes, key features, and emerging features—that organizations should evaluate when considering solutions in this market sector.
- Table stakes: Assumed value. These are features that all solutions in the sector support and therefore do not materially impact comparative assessment. Table stakes define minimum acceptable functionality for solutions under consideration.
- Key features: Differentiating value. These are features that significantly impact system operation and will be the basis on which organizations choose solutions for adoption. How vendors execute on these features sets products apart from each other and is vital in product selection.
- Emerging features: Future value. These are new or niche capabilities that can have downfield impact but do not significantly define the value of solutions today.
We also look at the nonfunctional requirements—business criteria—that organizations should consider when comparing solutions in this sector. These criteria help determine the impact a solution may have on the organization. Examples include cost, ease of use, and scalability. They are, in essence, strategic considerations, whereas the solution capabilities are tactical ones.
Evolution of Features
The relationship among table stakes, key features, and emerging features is central to our Key Criteria and Radar reports. These features evolve over time, with emerging features that become broadly adopted evolving into key features, while many key features become so ubiquitous that they graduate to table stakes. Figure 3 shows this evolution.
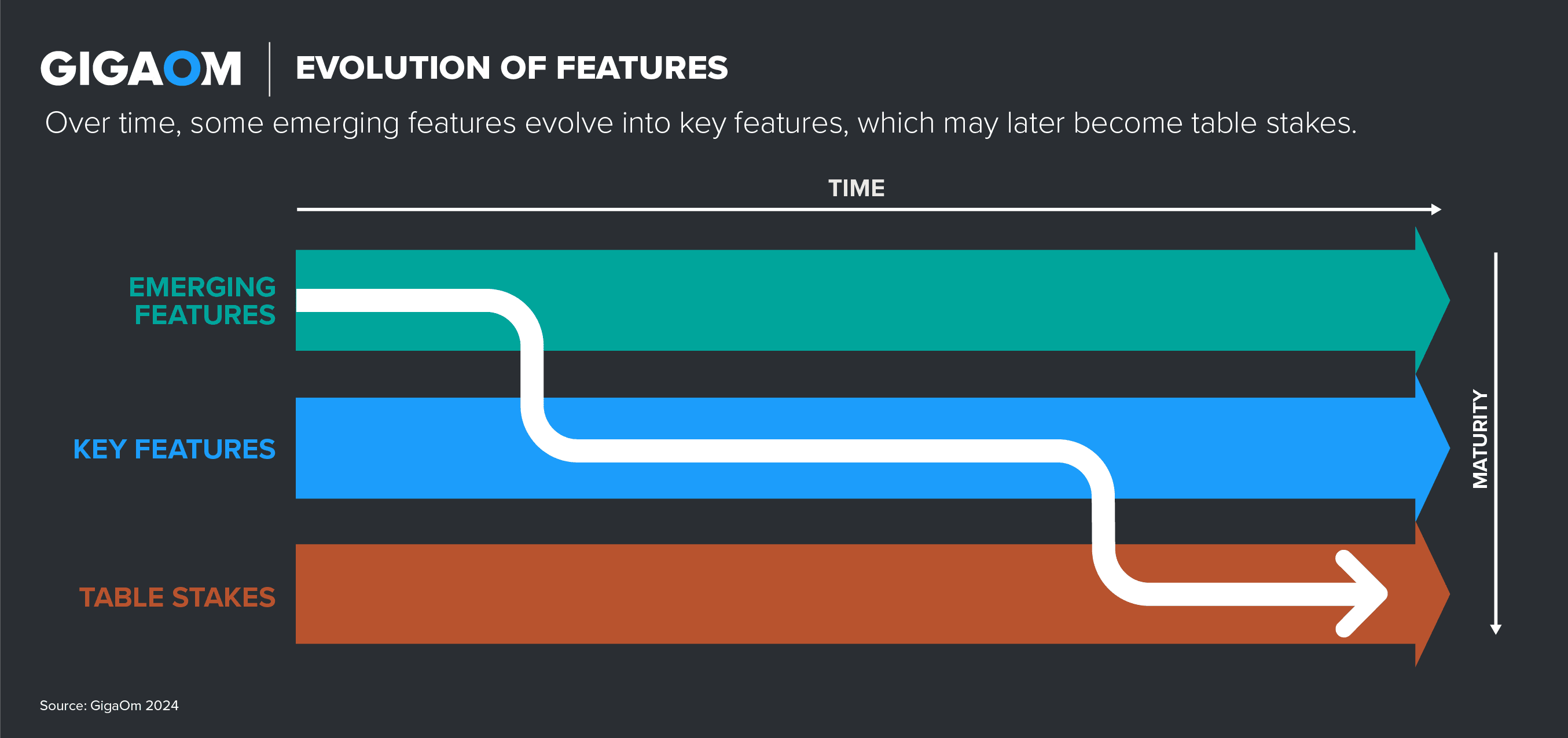
Figure 3. Progression of Solution Capabilities Over Time
Table Stakes
This report considers the following table stakes—features that all DSPM solutions should support. These features act as inclusion criteria for the companion Radar report:
- Automated data discovery
- Automated data classification
- Cloud platform integrations (including SaaS)
- Compliance reporting
- Agentless install for cloud
Automated Data Discovery
As data repositories move to the cloud, it can often introduce challenges in discovering data. Modern DSPM solutions can, once connected to an account with appropriate permissions, identify all data within a cloud tenant and auto-discover production data as well as unused and shadow data. It is not required for this auto-discovery capability to extend to on-premises repositories.
Automated Data Classification
A key part of DSPM is understanding what type of data is held by an organization. The ability to classify the type of information held is essential to building an effective data security posture. Any leading solution should be capable of classifying all data and at least identifying standard types of information such as financial, personal, and healthcare.
Cloud Platform Integrations (Including SaaS)
The modern organization is likely to have information stored in cloud data repositories. It is therefore important that leading DSPM solutions can integrate with those repositories. These should be infrastructure repositories that come in infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and platform as a service (PaaS) platforms as well as popular SaaS tools like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace. Leading solutions are capable of integrating with a good range of cloud repositories.
Compliance Reporting
A major use case for those looking at DSPM is to meet the demand of regulatory requirements, and understanding how data is stored and used is a critical part of data security posture. Solutions should be able to provide high-level compliance assessment reports showing how a business data posture compares to popular security frameworks.
Agentless Install for Cloud
When integrating with cloud repositories, customers do not wish to introduce latency, risk, or complexity to these environments. Therefore, solutions should provide agentless installation options such as APIs to integrate with these cloud-native repositories.
Key Features
This report considered the following key features—capabilities that some vendors offer but others may not fully support or don’t offer at all; these features are the basis on which organizations choose solutions for adoption. The key features for DSPM solutions are:
- Data mapping
- Data access intelligence
- Data lineage
- Security posture assessment
- Support for on-premises repositories
- Enterprise stack integration
- Data detection and response (DDR)
Data Mapping
When building a DSPM approach, an organization must understand what data it has. Leading solutions should be able to provide a comprehensive map of an organization’s data and the status of these data repositories, including outlining any potential risks to the data held within them.
Strong solutions should be capable of identifying production data, as well data that is orphaned and no longer used—shadow data that has been created outside of normal processes and that presents risks. Leading solutions will be capable of highlighting misconfigurations in repositories, including weak access permissions. Leading solutions will also be able to give insight into the flow of data to and from these repositories.
Data Access Intelligence
To understand data risk an organization must be able to build a detailed understanding of who or what is accessing data, when it is accessed, and what data is accessed. Leading solutions should be able to provide insight into these data access questions. Tools should integrate with popular identity platforms such as Entra ID to ensure it can have detailed insight into user information. Leading solutions will add to this additional intelligence; for example, with the ability to look for unusual behavior and, while not natively carrying out mitigation actions, the ability to alert or integrate with tools that can alert. The best solutions will be able to enforce mitigation actions when identifying risks.
Data Lineage
To understand data risk, organizations must be able to understand the data lifecycle. Therefore, a DSPM solution must help illustrate how data moves through a data pipeline and how it is impacted, accessed, and changed through that process.
Understanding the flow of data is an essential part of data security. Good solutions will be able to provide insight into the data lifecycle. The better solutions will help in understanding lineage by providing clear visualization of data flows, showing dependencies between data sources and highlighting the impacts of change. The very best solutions will provide detail in areas such as how data has been derived, calculated, and transformed.
Security Posture Assessment
Fundamentally, those organizations deploying DSPM must understand their posture in comparison to their desired security state. Leading solutions should be able to clearly show this so that customers can quickly understand posture and the steps needed to maintain or improve it.
Good solutions will provide an assessment of posture against all managed data repositories. The more basic solutions may only display information such as a data inventory, its location, and the type and sensitivity of the information held. More advanced solutions will provide more detailed insight into the information held within any piece of data, will show posture against a broad range of leading data security frameworks, and will allow customers to build custom frameworks against which to measure posture. Leading solutions can also provide more detailed guidance on improving security, such as showing how data security techniques like masking and encryption will improve posture.
Support for On-Premises Repositories
While many organizations have embraced the cloud, much business data remains on-premises. Leading DSPM solutions should be capable of including on-premises data repositories in their insights and posture assessments. Solutions that offer this should be able to include unstructured data such as file shares alongside structured data sets like more traditional databases. The best solutions will offer comprehensive coverage for on-premises repositories.
Enterprise Stack Integration
No technology solution in the modern enterprise, especially in the security space, can be a silo. For the solution to be a successful part of day-to-day operations, it must integrate with existing elements of the current technology stack. This will allow it to be part of existing workflows and add value to existing investments.
Enterprise security solutions cannot exist in isolation and must integrate with the enterprise technology stack including tools such as SIEM, SOAR, ITSM, endpoint detection and response (EDR), extended detection and response (XDR), and identity providers (IdP). The best solutions will offer comprehensive coverage including a good range of prebuilt integrations to lower the overhead of integrating these solutions into the broader ecosystem. When there is a need for custom integrations, leading solutions will also provide support for building them, either by the customer within the platform or offered as a professional service by the vendor.
DDR
The primary goal of a DSPM solution is to provide insight into current posture and guidance on improvement. In the rapidly evolving data threat landscape, solutions must be able to quickly identify active threats and automate their mitigation, which will help reduce threat and breach impact.
Good solutions will be capable of providing data threat detection and alerting security operations center (SOC) analysts to the threat and provide guidance on how to deal with it. Better solutions may add to this the ability to integrate with third-party tools to help automate the response and carry out mitigation actions. The best solutions will provide the ability to orchestrate response either in conjunction with other tools or natively within the platform, allowing customers to build complex response runbooks to quickly nullify data security threats.
Emerging Features
This report considers the following emerging features—capabilities that are not yet widespread but we expect will become widely relevant over the next year or two:
- Impact analysis
- AI data interaction
Impact Analysis
When a solution identifies a potential risk to an organization’s data set, it is hugely valuable for the organization to clearly understand the broader impact that these risks will have should they be exploited. Vendors are starting to highlight the broader radius of impact of any risk. This can include providing indications of cost of impact, which can also be a useful metric for non-IT teams.
AI Data Interaction
Increasingly, organizations are using AI learning models within their organizations. These learning models will access data across repositories. This presents risks to an organization, from oversharing of information to poor-quality data feeding the learning models. DSPM solutions are starting to invest in tooling to help organizations more effectively adopt AI with features from data cleansing to building guardrails to reduce the risk of oversharing. We expect to see this continue to develop into a key feature over the next 12 months.
Business Criteria
Next, we look at business criteria—non-functional requirements that impact a purchase decision and determine a solution’s impact on an organization. The business criteria for DSPM solutions are:
- Cost
- Ease of use
- Ease of management
- Security posture
- Flexibility
Cost
Any business, when evaluating technology, must understand the cost of the investment. This is reflected in the price of a license or service as well as in its adoption and running costs. Vendors that can help customers drive cost efficiency will have an attractive offering.
Solutions that help lower costs will provide broad repository support to ensure customers get the most data coverage within a single product. These solutions will also help to control operating costs by integrating well into the existing stack, allowing DSPM to be part of existing operations. The vendor will also make technology evaluation easy and offer transparent solution costs to help users quickly understand the scale of investment required.
The key features that most impact cost are data mapping, support for on-premises repositories, and enterprise stack integration.
Ease of Use
Driving effective adoption is key to the success of any IT project. Adoption can be helped in a number of ways, from good integration with existing platforms to the ability to include the new solution in existing workflows. Solutions that ease adoption by operations teams and users will add value while minimizing cost.
Solutions that provide broad coverage and integration with existing environments will be easier to adopt, making them easier to use. Solutions that offer good automation of repository discovery will also help ease adoption burden by reducing the need for prediscovery and configuration. Providers that ease onboarding by way of training and support also help to ease the adoption and operational overhead.
The key features that most impact ease of use are security posture assessment, support for on-premises repositories, and enterprise stack integration.
Ease of Management
Data security is already complex—adding new solutions should limit additional complexity. Businesses will welcome solutions that ease management, provide central administration and reporting, and automate repetitive tasks. Vendors can also facilitate this by providing services such as support, training, and proactive account management, all helping to ease the overall management burden.
To ease the management overhead, solutions should provide broad coverage across all repositories, including on-premises, to reduce gaps in overall data security posture. They will map data clearly and accurately to help build understanding around data, what it contains, and who has access to it. Solutions with clear interfaces, workflows, and the potential to automate tasks also help with ease of management. Solutions can ease management by making data security posture clear, highlighting risks, and providing clarity around mitigation steps.
The key features that most impact ease of management are data mapping, data access intelligence, support for on-premises repositories, and enterprise stack integration.
Security Posture
Customers should be able to measure the success of their investment in DSPM tools. To do this, solutions should help a customer identify its current security posture, highlight gaps in this position, and provide clear advice on how to improve this position. Solutions that can show the baseline and ways to measure improvement will greatly help customers on their route to better data security.
To help develop a good understanding of security posture, customers will need tools that begin by providing them with a good understanding of current data, what it contains, and where security risks can be found. Many organizations have requirements to meet regulatory demands. Solutions that provide clarity of data posture against regulatory frameworks will also help businesses to both improve security posture and ensure it meets business compliance goals.
The key features that most impact security posture are data mapping, data access intelligence, data lineage, and security posture assessment.
Flexibility
Customer environments differ and change. Security tools must be flexible as well, offering different deployment models and adoption techniques, as well as commercial flexibility to fit a broad range of potential customer licensing needs.
Businesses need solutions that are flexible to meet evolving demands. Technically, solutions that offer broad support across cloud and on-premises repositories will help, as will solutions that can integrate well with a broad range of existing enterprise operational tools. This will also include installation options that support a business’s requirements around technology as well as compliance. Equally important is a vendor’s approach to flexibility. They should provide flexible commercial models that can, for example, scale up and down as demands change.
The key features that most impact flexibility are support for on-premises repositories and enterprise stack integration.
4. Analyst’s Outlook
DSPM is an evolving part of the data security market. It brings together several strands that include data discovery, data classification, data compliance, and access control. In these early stages of development, customers should expect some inconsistency and difference of interpretation in some aspects of the solution, especially when it comes to the security posture assessment itself. While measuring against known frameworks is helpful, applying risk scores is currently a matter of interpretation for vendors.
Some of the vendors in this space will have grown from areas such as cloud security posture management (CSPM) and, as such, will have a cloud focus for data repositories. However, many organizations still have large amounts of on-premises data that will need to be captured, and they should consider these needs when evaluating vendor capabilities.
The purpose of this research is to identify solutions that help with data security posture, and as such, it is not focused on platforms that can deliver threat mitigation and reduction. Still, potential customers should consider how they will enforce data security controls and what part a DSPM platform will play in that. Do they need automation natively in the platform or via integration with existing enterprise orchestration tools?
While DSPM is a developing area, this approach to data security requires a level of business maturity. The application of data security controls often needs a cultural shift in the way an organization thinks about and uses data. Organizations must consider this impact and how to address it. DSPM projects require business-wide support and should not be driven by IT alone.
The requirement for change in an organization’s operational approaches also means a strong business case is required to drive it. Adopters of this technology are likely to be in heavily regulated industries such as finance, public sector, and healthcare. A rapidly growing use case for consideration is the adoption of AI. The data fed to AI learning models must be appropriate and secure to ensure these tools do not present data security risks.
The companion GigaOm Radar report examines 13 of the top DSPM solutions in the market. The report compares offerings against the key features, emerging features, and business criteria outlined in this Key Criteria report. Prospective buyers should use both reports to select the best fit for their business and use case requirements.
To learn about related topics in this space, check out the following GigaOm Key Criteria reports:
- GigaOm Key Criteria for Evaluating Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions
- GigaOm Key Criteria for Evaluating CSPM Solutions
- GigaOm Key Criteria for Evaluating Data Access Governance Solutions
5. Methodology
*Vendors marked with an asterisk did not participate in our research process for the Radar report, and their capsules and scoring were compiled via desk research.
For more information about our research process for Key Criteria and Radar reports, please visit our Methodology.
6. About Paul Stringfellow
Paul Stringfellow has more than 25 years of experience in the IT industry helping organizations of all kinds and sizes use technology to deliver strong business outcomes. Today, that work focuses mainly on helping enterprises understand how to manage their data to ensure it is protected, secure, compliant, and available. He is still very much a “hands-on” practitioner and continues to be involved in a diverse range of data projects. Paul has been recognized across the industry and has spoken at many industry, vendor, and community events. He writes for a number of industry publications to share his enthusiasm for technology and to help others realize its value.
Paul hosts his own enterprise technology webcast and writes regularly on his blog.
7. About GigaOm
GigaOm provides technical, operational, and business advice for IT’s strategic digital enterprise and business initiatives. Enterprise business leaders, CIOs, and technology organizations partner with GigaOm for practical, actionable, strategic, and visionary advice for modernizing and transforming their business. GigaOm’s advice empowers enterprises to successfully compete in an increasingly complicated business atmosphere that requires a solid understanding of constantly changing customer demands.
GigaOm works directly with enterprises both inside and outside of the IT organization to apply proven research and methodologies designed to avoid pitfalls and roadblocks while balancing risk and innovation. Research methodologies include but are not limited to adoption and benchmarking surveys, use cases, interviews, ROI/TCO, market landscapes, strategic trends, and technical benchmarks. Our analysts possess 20+ years of experience advising a spectrum of clients from early adopters to mainstream enterprises.
GigaOm’s perspective is that of the unbiased enterprise practitioner. Through this perspective, GigaOm connects with engaged and loyal subscribers on a deep and meaningful level.
8. Copyright
© Knowingly, Inc. 2024 "GigaOm Key Criteria for Evaluating Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) Solutions" is a trademark of Knowingly, Inc. For permission to reproduce this report, please contact sales@gigaom.com.
